The company relies on a high degree of brand awareness, fine product quality, convergence of multiple strong advertising media power, and through the integration of capital, knowledge, talent technology, channels, information operations.
The Role of Non-Stick Cookware in Modern Kitchens
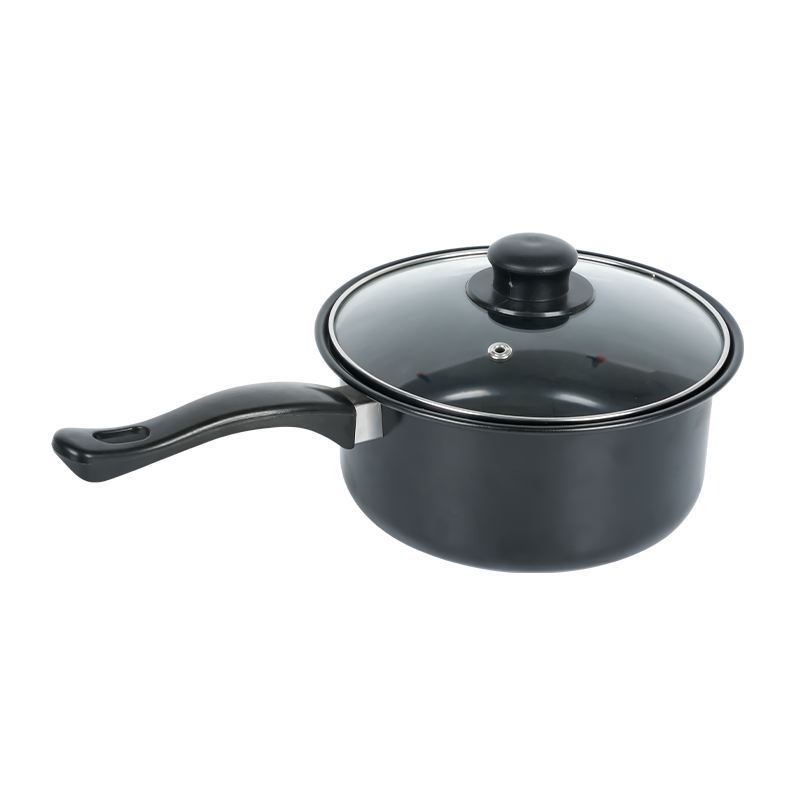
A Cooking Pan Non Stick is now a staple in both household and professional kitchens, valued for its convenience and ease of maintenance. By preventing food from adhering to the pan’s surface, it enhances cooking efficiency and simplifies cleaning. However, the quality and longevity of such pans depend on several technical and material factors, including coating composition, heat tolerance, and manufacturing precision. Understanding how these variables interact helps consumers and manufacturers improve performance and safety.

Material Selection and Structural Foundation
The durability and functionality of a non-stick pan begin with its core materials.
- Base Metal Choice: Aluminum and stainless steel are commonly used. Aluminum provides good heat conduction, while stainless steel offers structural strength and compatibility with induction cooktops.
- Thickness Control: A uniform base thickness prevents hot spots, ensuring even heating during cooking. Too thin a layer causes warping under high heat, while excessive thickness slows temperature response.
- Surface Preparation: Before coating application, the metal surface is sandblasted or chemically treated to improve adhesion between the base and the non-stick layer.
Coating Composition and Application Techniques
The heart of a Cooking Pan Non Stick lies in its surface coating technology.
- Material Types: Common coatings include PTFE-based (Teflon) layers, ceramic coatings, and diamond-infused composites. Each type offers a different balance between heat resistance and chemical stability.
- Layering Process: Multi-layer coatings enhance scratch resistance and prevent peeling. Typically, two to three layers are applied, followed by thermal curing to strengthen molecular bonding.
- Safety Standards: Reputable manufacturers comply with FDA and EU food-contact safety regulations, ensuring no harmful chemicals are released at high temperatures.
Heat Distribution and Cooking Efficiency
Thermal performance plays a crucial role in cooking results.
- Uniform Heating: A well-engineered base distributes heat evenly, preventing localized burning or undercooked spots.
- Energy Efficiency: Non-stick surfaces reduce the need for oil or butter, promoting faster heating and energy savings during daily cooking.
- Temperature Tolerance: High-quality coatings maintain integrity up to around 260°C, while poor-quality ones degrade and release fumes at lower thresholds.
Resistance to Wear and Surface Longevity
One of the main concerns for users is how long the non-stick effect lasts.
- Scratch Resistance: Using silicone, wooden, or nylon utensils decreases surface damage. Metal tools often accelerate wear, reducing lifespan.
- Cleaning Practices: Gentle cleaning with soft sponges and mild detergents preserves coating quality. Harsh scrubbing or dishwasher exposure can cause micro-abrasions.
- Reinforced Coatings: Advanced models use mineral or titanium reinforcement to improve durability under daily use conditions.
Environmental and Health Considerations
Sustainability and health safety are now key factors influencing product design.
- Eco-Friendly Coatings: Ceramic and water-based coatings have gained popularity as alternatives to traditional PTFE, which may involve fluorinated compounds.
- Reduced Oil Usage: The low-adhesion surface helps minimize fat consumption, aligning with healthier cooking practices.
- Recyclable Materials: Some manufacturers now produce pans with recyclable metal bases and replaceable handles to reduce waste.
Manufacturing Innovation and Quality Assurance
Modern production methods are making non-stick cookware more reliable than ever.
- Automation and Precision: Robotic coating systems ensure even application, reducing human error and coating inconsistencies.
- Quality Testing: Each batch undergoes abrasion, adhesion, and thermal resistance testing before packaging.
- Batch Traceability: Advanced labeling systems allow customers to trace the manufacturing lot, improving product accountability and consumer trust.
Market Trends and Consumer Preferences
As cooking styles evolve, so do consumer expectations.
- Design Variety: Manufacturers now offer different sizes, depths, and shapes suited to specific cuisines such as stir-frying, sautéing, or simmering.
- Color and Aesthetics: Exterior coatings come in multiple colors, enhancing kitchen appeal without sacrificing functionality.
- Value Perception: Consumers increasingly look for the balance between price, longevity, and eco-safety when selecting non-stick cookware.
 English
English русский
русский Español
Español



