The company relies on a high degree of brand awareness, fine product quality, convergence of multiple strong advertising media power, and through the integration of capital, knowledge, talent technology, channels, information operations.
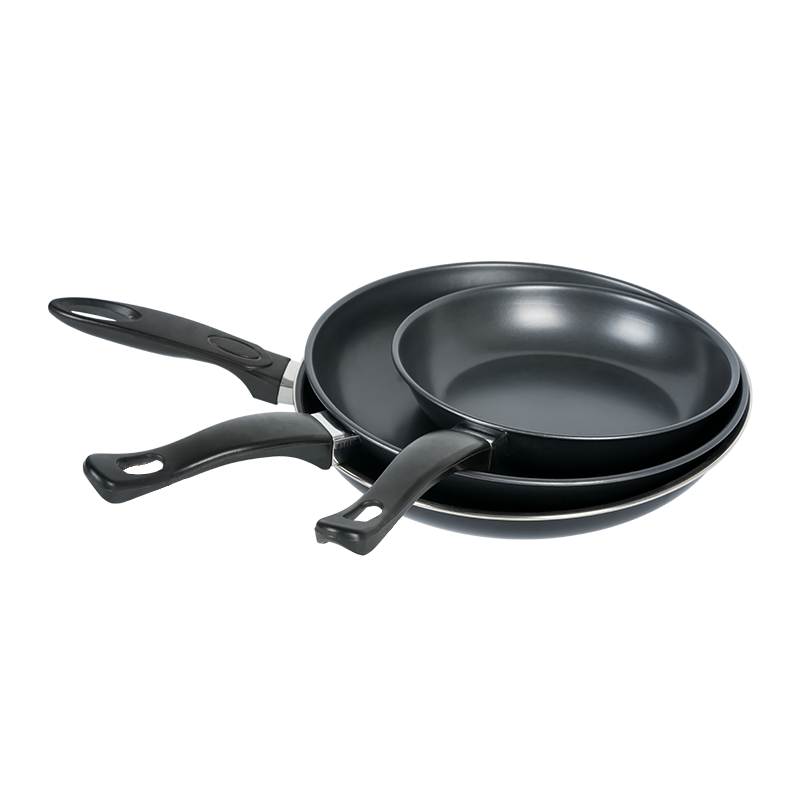
Cooking Pan Non Stick is widely appreciated for its convenience, easy cleaning, and low-oil cooking capability. However, one of the common questions among home cooks is whether non-stick pans distribute heat evenly and whether they are prone to hot spots that cause localized burning or sticking. Understanding how heat transfer works in non-stick cookware helps users achieve consistent cooking results and avoid common pitfalls like unevenly cooked meals or burnt areas.

Material Composition and Heat Conductivity
The performance of a non-stick pan largely depends on its base material. Most non-stick pans feature an aluminum core, sometimes combined with stainless steel, because aluminum conducts heat quickly and evenly. This design ensures that the pan heats rapidly and distributes heat across the cooking surface. Despite this, variations in thickness or quality of the metal base can cause uneven heat zones. Cheaper or thinner pans may develop localized hot spots, causing some areas of food to cook faster and potentially burn, while other areas remain undercooked.
Impact of Non-Stick Coating on Heat Transfer
The non-stick coating itself, such as PTFE or ceramic, is primarily designed to prevent food from adhering to the surface. While the coating does not significantly conduct heat, it can slightly influence the uniformity of cooking. High-quality non-stick coatings are applied evenly, helping to maintain consistent thermal contact between the food and the pan surface. Lower-quality coatings may have slight imperfections or inconsistencies, which can exacerbate uneven heating and increase the risk of localized sticking or burning.
Cooking Techniques to Avoid Hot Spots
Even with a high-quality non-stick pan, improper cooking techniques can result in uneven heating. Using too high heat, leaving food unattended, or crowding the pan can create temperature variations across the surface. Preheating the pan gradually and using moderate heat levels helps ensure the entire cooking area reaches a consistent temperature. Additionally, stirring, rotating, or moving food during cooking can reduce the impact of any minor heat irregularities.
Comparison with Traditional Cookware
Compared to stainless steel or cast iron pans, non-stick cookware often heats faster due to the aluminum base, but may be slightly more susceptible to hot spots if the base is thin or poorly constructed. Cast iron, while slower to heat, provides a very consistent and stable thermal distribution once fully heated. Stainless steel pans may have uneven heat unless they include an aluminum or copper core. Therefore, selecting a well-constructed non-stick pan with a thick aluminum base can offer performance similar to or better than some traditional cookware in terms of heat distribution.
Practical Recommendations for Users
To ensure even cooking with Cooking Pan Non Stick, users should choose pans with a thick, high-quality aluminum core and a uniform non-stick coating. Avoid cooking at extremely high temperatures and regularly monitor food during the cooking process. Rotating the pan or stirring ingredients can compensate for minor hot spots. Proper care, such as avoiding warping by heating an empty pan excessively, also helps maintain consistent thermal performance over time.
Achieving Uniform Cooking Performance
The evenness of heat distribution in Cooking Pan Non Stick depends on the quality of materials, coating, and user practices. While inferior pans may be prone to localized hot spots and uneven cooking, well-designed non-stick pans with a thick aluminum core provide reliable, uniform heat transfer. By understanding the relationship between pan construction and cooking technique, users can reduce burning or sticking and achieve suitable results for everyday meals.
 English
English русский
русский Español
Español



